Multi-directional die forging is a precision forging technology performed on multi-directional forging hydraulic presses. Its core principle lies in the combination of extrusion and forging to shape complex components. The deformation process primarily relies on extrusion, integrating the advantages of traditional forging while introducing innovative techniques. Compared to conventional forging and split-die forging processes, multi-directional die forging demonstrates significant technical and economic advantages, particularly in material utilization, forging performance, production efficiency, and adaptability.
Multi-directional die forging involves the simultaneous or sequential application of multiple punches from different directions to extrude or pierce a blank, utilizing triaxial compressive stress for plastic deformation. This allows for the production of complex forgings in a single heating and press cycle. It is especially suitable for forgings with internal cavities or intricate shapes, such as concave-convex geometries.
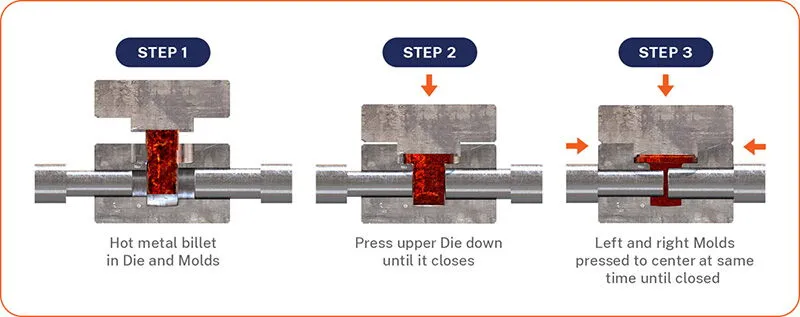
The basic process flow of multi-directional die forging includes:
Blank Preparation: Selecting appropriate metal materials and heating them to the optimal forging temperature.
Die Closure: Multiple punches apply pressure from different directions to shape the blank into the desired forging form.
Plastic Deformation: The blank undergoes plastic deformation under triaxial compressive stress to complete the forming process.
Cooling and Removal: After cooling, the forging is removed from the die and subjected to subsequent processing.
The hallmark of this process is its ability to achieve complex shaping in a short time through extrusion, making it ideal for forgings with internal cavities, lateral structures, or intricate shapes.
Multi-directional die forging possesses several distinctive features that set it apart in the forging industry.
Unlike traditional forging, multi-directional die forging generates minimal flash waste. Forgings can be designed as hollow, reducing the need for draft angles and saving 30%-50% of metal material. The closed-die structure further minimizes material waste, enhancing metal utilization.
During multi-directional die forging, metals are formed under high hydrostatic stress and significant equivalent strain, resulting in denser microstructures and easier defect elimination. The flow lines of the forging are distributed along its contour, significantly improving mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. Compared to traditional methods, the strength of forgings can increase by over 30%.
Multi-directional die forging reduces the number of steps required, often completing the forming process in a single heating and press cycle. This cuts the number of operations by more than 50%, significantly boosting efficiency. The simplicity of blank shapes lowers preparation costs, shortens production cycles, reduces energy consumption, and minimizes mold investment, thereby lowering overall production costs.
Multi-directional die forging is not only suitable for common metals but also for special alloys with narrow temperature ranges and low plasticity. The process significantly enhances plasticity, enabling effective deformation of high-alloy steels and special alloys under triaxial compressive stress. This makes it ideal for manufacturing high-performance, complex components.
The molds used in multi-directional die forging are simple yet ingeniously designed, improving production efficiency and extending mold lifespan. Compared to traditional open-die forging, the molds are more cost-effective and durable, reducing the overall production cost of forgings.
Compared to traditional forging methods, multi-directional die forging offers substantial economic advantages.
Traditional forging often wastes significant metal material in flash, whereas multi-directional die forging eliminates flash or reduces draft angles, greatly improving material utilization. In practice, this can reduce material waste by 15%-30%.
With fewer steps, simpler blanks, and reduced heating cycles, multi-directional die forging significantly cuts energy consumption. Additionally, the precise dimensions of the forgings reduce the need for subsequent machining, further lowering production costs. Material and energy consumption can typically be reduced by over 20% compared to traditional methods.
The streamlined process of multi-directional die forging shortens production cycles. While traditional forging often requires multiple heating and processing steps, multi-directional die forging typically achieves forming in a single cycle. By reducing heating cycles and simplifying processes, production efficiency is markedly improved.
Due to its unique advantages, multi-directional die forging is widely used in various fields, particularly in the manufacturing of high-performance and complex components. Key application areas include:
Oil and Chemical Industries: Multi-directional die forging is used to produce complex valve bodies, pipe fittings, and hollow structural components that meet high-pressure, high-temperature, and corrosion-resistant requirements.
Power Industry: It is employed in manufacturing shafts and support components for power equipment, ensuring high strength and stability.
Aerospace and Defense: Multi-directional die forging is extensively used in producing complex parts for aircraft engines and military equipment, where high material strength and reliability are critical.
Automotive Industry: It is suitable for manufacturing various automotive components, such as suspension systems and engine parts, particularly for lightweight, high-strength applications.
Multi-directional die forging is an advanced forging technology that combines precision, efficiency, energy savings, and material conservation. It is particularly well-suited for producing complex, high-performance forgings. Through precise triaxial extrusion, it significantly enhances material utilization, improves forging performance, reduces production costs, and boosts production efficiency. As a result, multi-directional die forging has broad application prospects in industries such as oil, chemicals, power, aerospace, and defense, making it an ideal choice for manufacturing high-value, complex components.